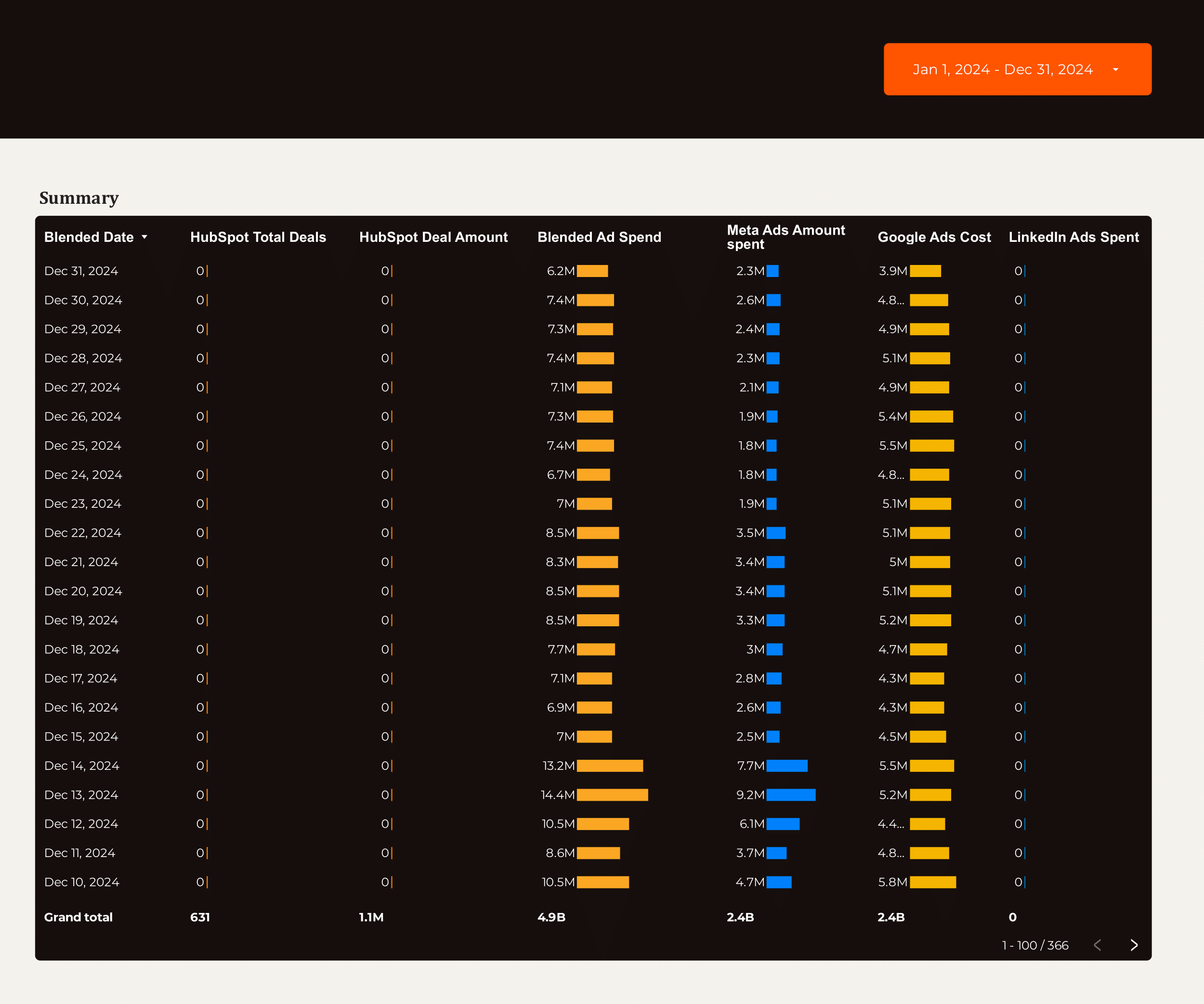
Lead generation Dashboard template
The Lead Generation Dashboard Template is designed for B2B marketers and sales teams to streamline their lead management process. This template integrates with popular platforms such as Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads, Facebook Ads, and HubSpot, providing a centralized view of your lead generation efforts.
Utilize data from Google Analytics 4 to track and analyze the performance of your campaigns. The dashboard offers insights into:
- Lead Sources: Identify which channels are driving the most leads.
- Conversion Rates: Monitor the effectiveness of your PPC campaigns.
- CRM Integration: Seamlessly connect with HubSpot to manage and nurture leads.
This template is essential for businesses looking to optimize their B2B lead generation strategy by leveraging data from multiple advertising and analytics platforms.
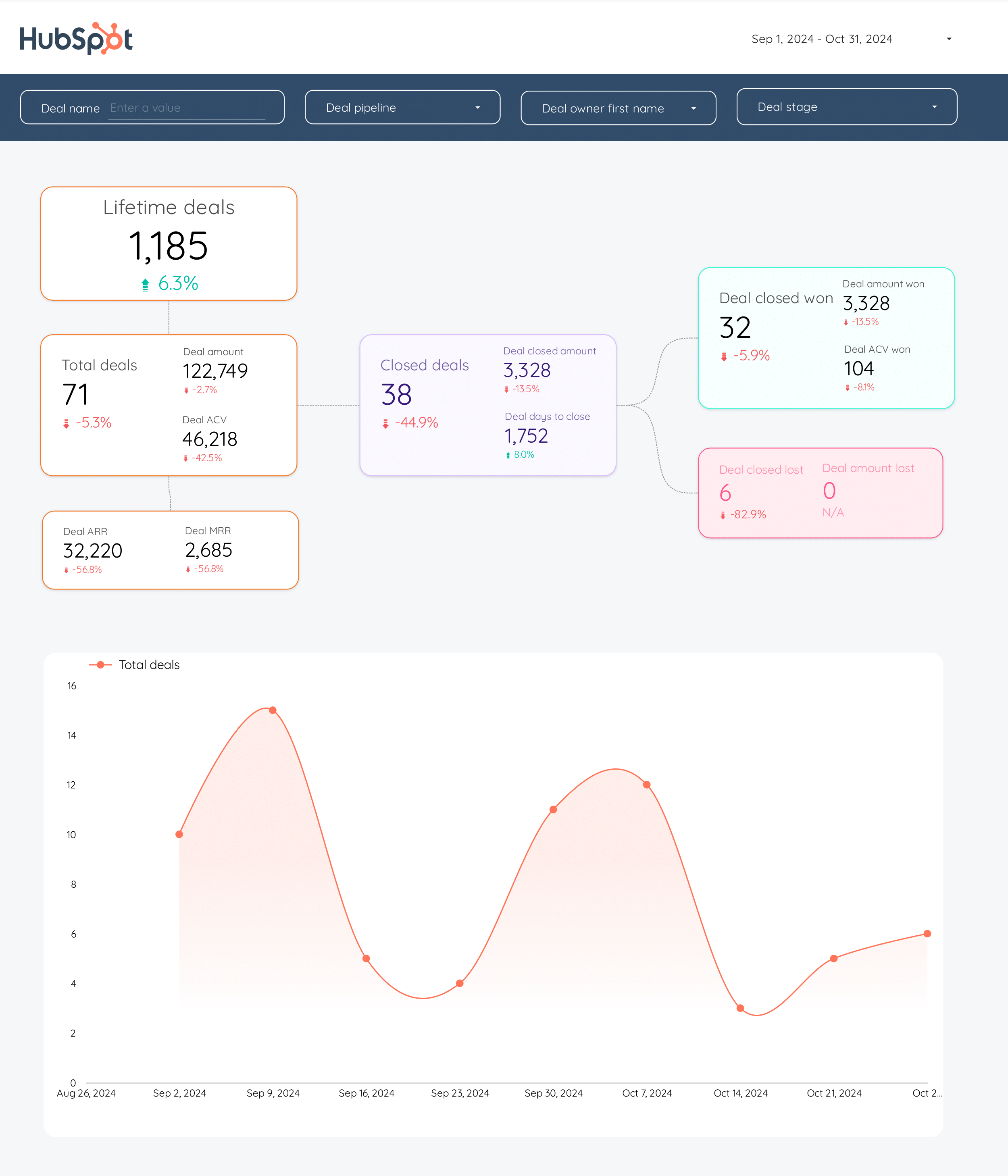
HubSpot Dashboard template
The HubSpot Dashboard Template is designed for B2B companies focusing on CRM and Email Marketing. This template provides a structured view of your marketing and sales data, enabling you to track and analyze your funnels and inbound marketing efforts effectively.
With this dashboard, you can:
- Monitor lead generation and conversion rates through detailed funnel analysis.
- Track email campaign performance metrics, including open rates and click-through rates.
- Analyze customer interactions and engagement within the HubSpot CRM.
Utilize this template to align your marketing strategies with your business objectives, ensuring a data-driven approach to inbound marketing.
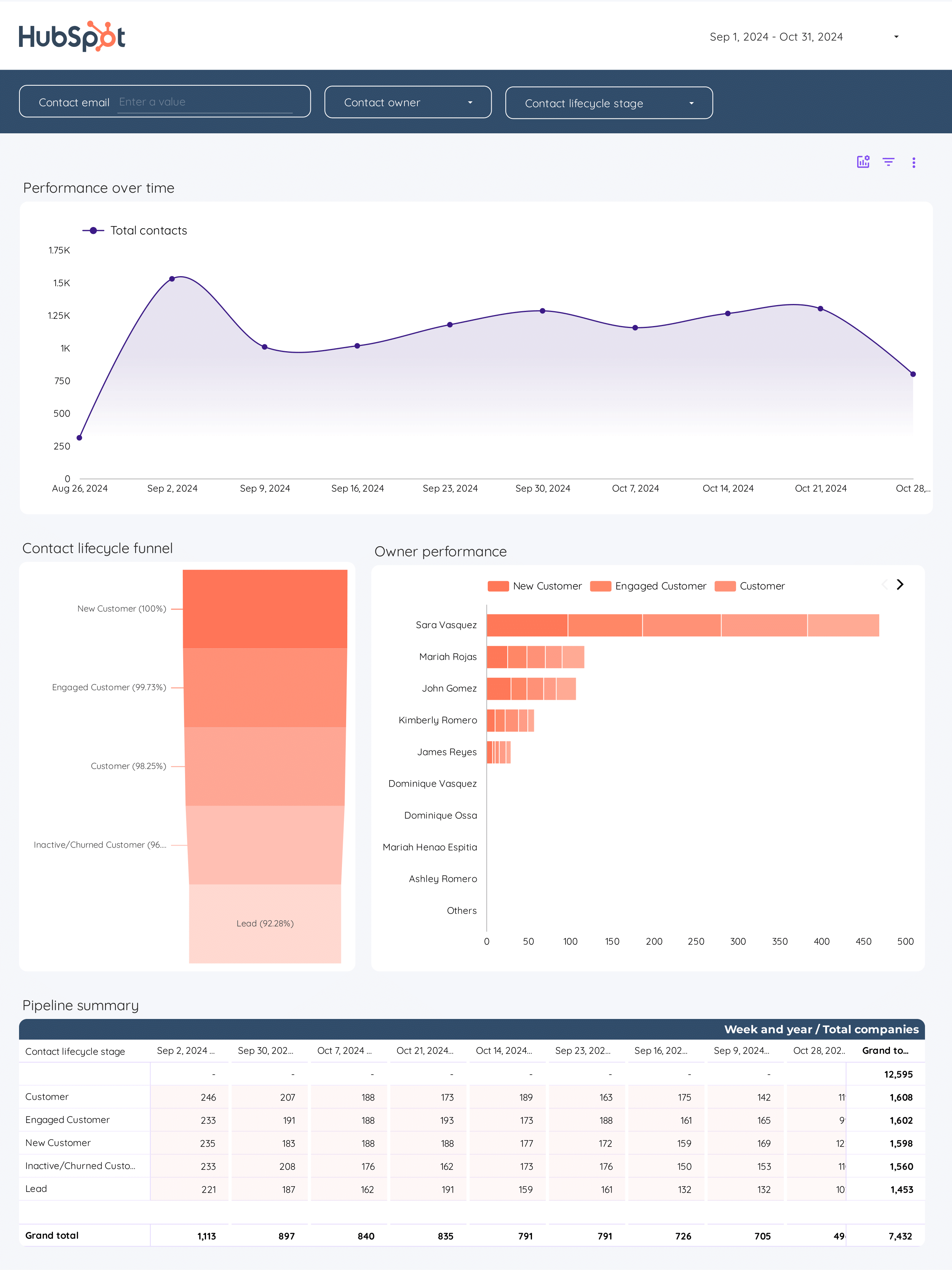
CRM Dashboard template
The CRM Dashboard Template is designed for B2B companies focusing on CRM and Email Marketing strategies. This template integrates seamlessly with platforms like HubSpot, Mailchimp, and ActiveCampaign, providing a centralized view of your sales and marketing activities.
Utilize this dashboard to:
- Track and manage sales pipelines efficiently.
- Monitor email marketing campaigns and their performance metrics.
- Analyze customer interactions and engagement levels.
- Access real-time data from HubSpot and other CRM tools.
This template serves as a foundational base for businesses aiming to streamline their CRM processes and optimize their email marketing efforts.
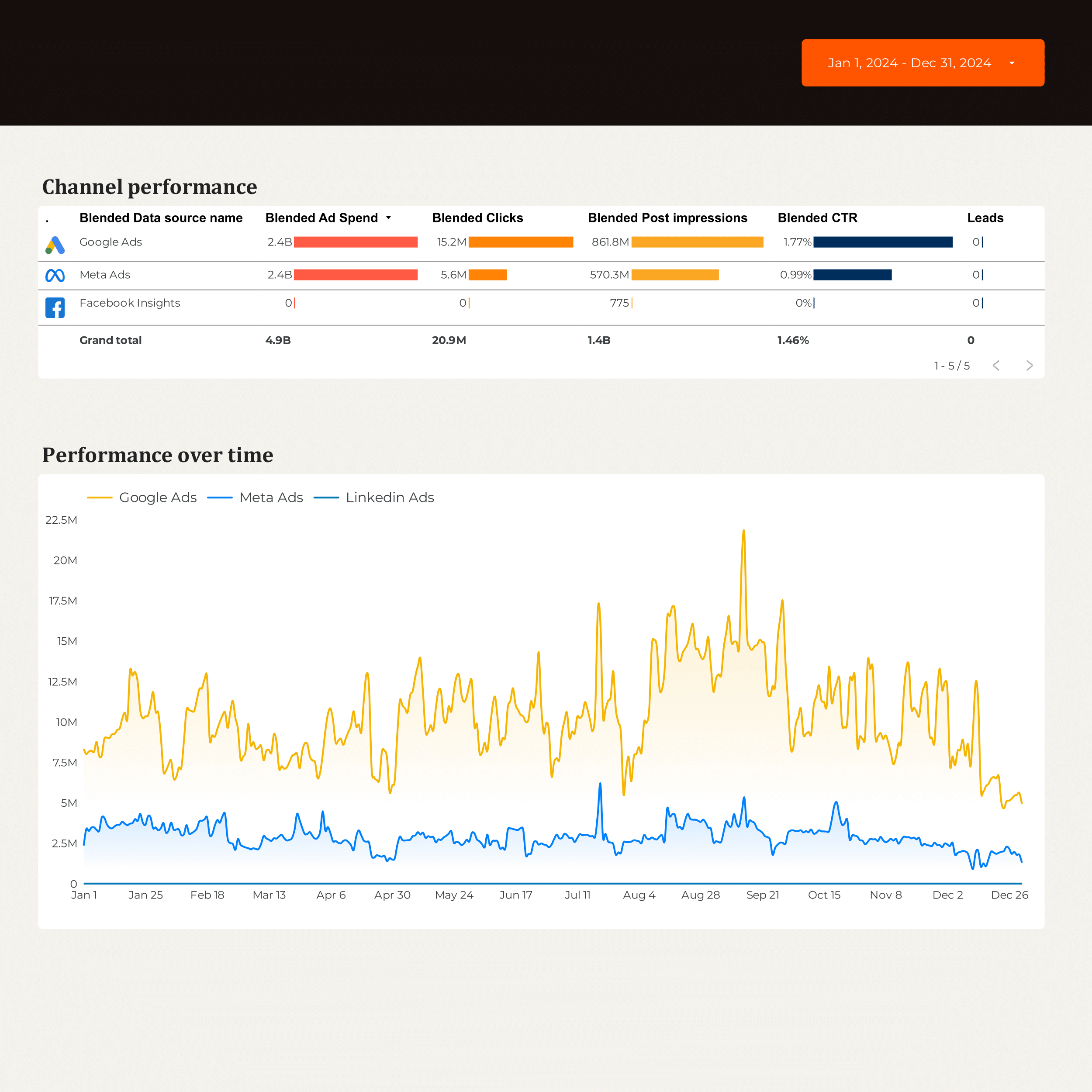
B2B Marketing performance Dashboard template
The B2B Marketing Performance Dashboard template provides a centralized view of your marketing efforts across multiple channels. This dashboard integrates data from CRM systems, Email Marketing platforms, and advertising networks to offer a complete picture of your marketing performance.
Track and analyze data from:
- HubSpot for CRM insights and lead management.
- Google Ads and Facebook Ads for PPC campaign performance.
- LinkedIn Ads to monitor B2B engagement and conversions.
- Google Analytics 4 for web traffic and user behavior analysis.
This dashboard template allows you to monitor campaign performance, lead generation, and ROI metrics, providing actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
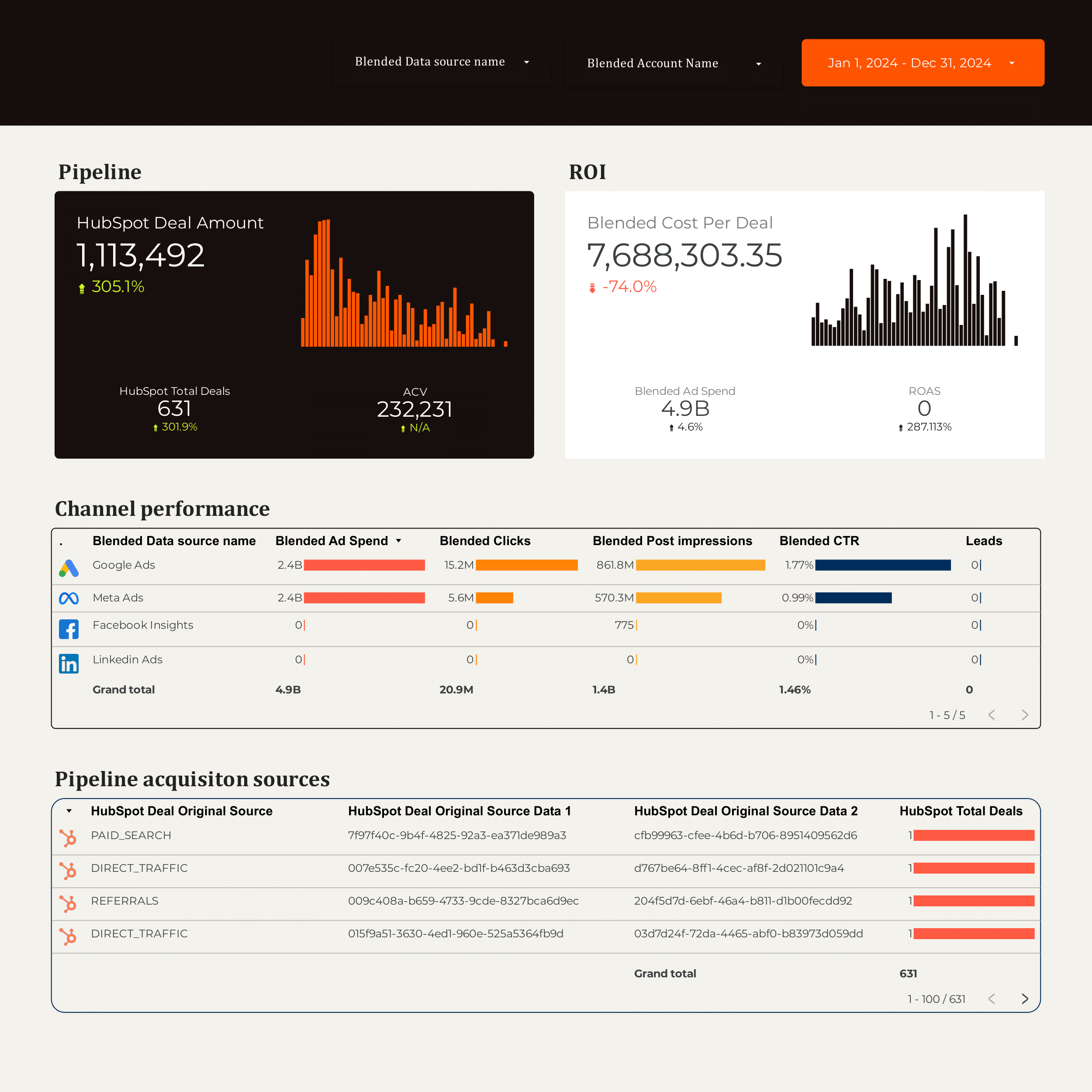
B2B Dashboard template
The B2B Dashboard template integrates with HubSpot, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads, and Google Analytics 4 to provide a centralized view of your marketing and sales data.
Utilize this dashboard to track and analyze:
- CRM Data from HubSpot for lead management and sales performance.
- PPC Campaigns across Facebook, Google, and LinkedIn Ads to monitor ad spend and ROI.
- SEO Metrics to assess organic search performance and traffic sources.
- Website Analytics through Google Analytics 4 for user behavior insights and conversion tracking.
This template is designed for B2B marketers seeking to streamline data from multiple platforms into a single, actionable interface.
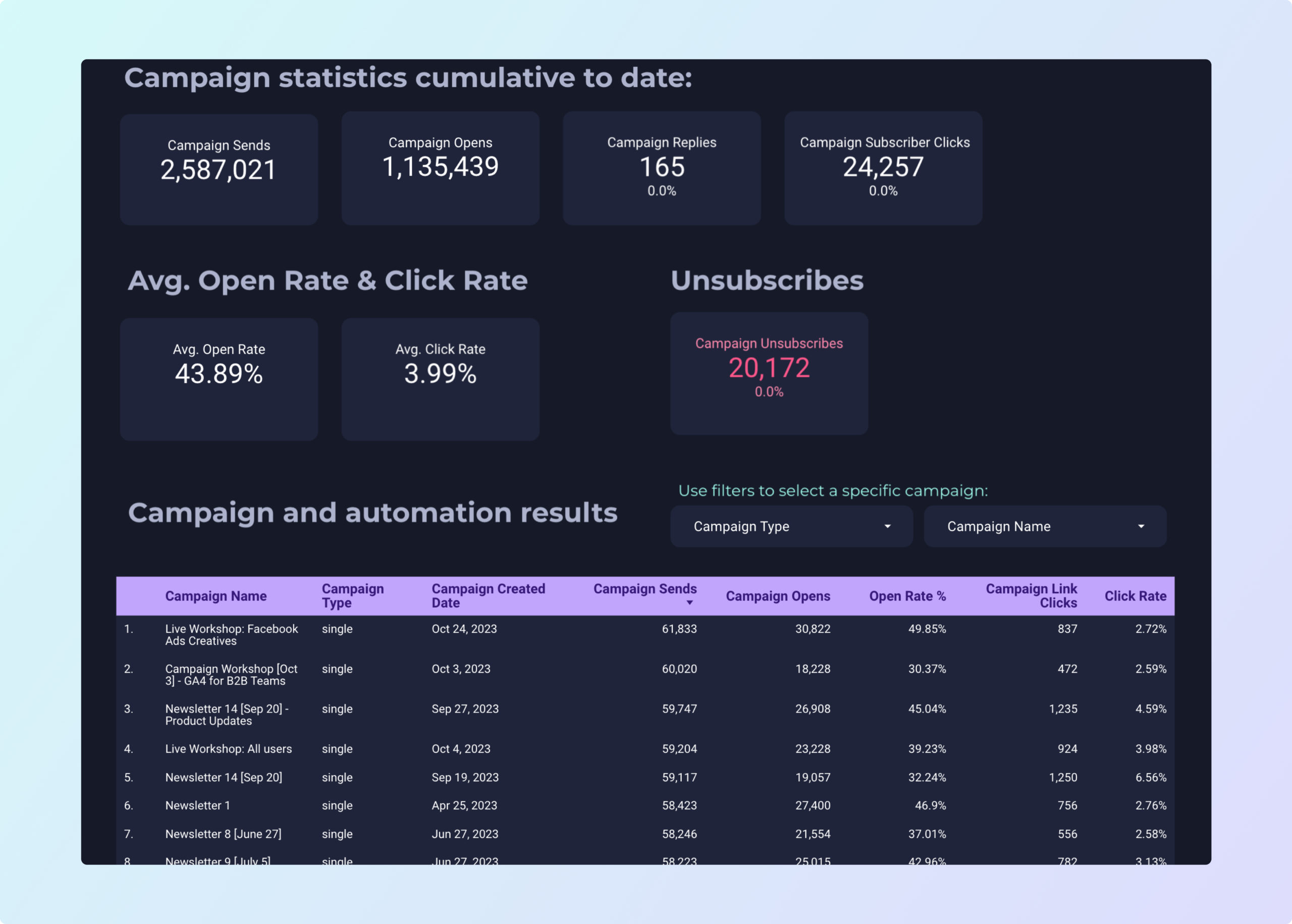
ActiveCampaign Dashboard template
The ActiveCampaign Dashboard Template is designed for B2B companies focusing on CRM and Email Marketing. This template integrates seamlessly with ActiveCampaign, providing a robust platform for managing customer relationships and automating marketing efforts.
With this dashboard, businesses can:
- Monitor and analyze email marketing campaigns in real-time.
- Track customer interactions and engagement metrics.
- Automate marketing workflows to streamline operations.
The template supports automation features, allowing users to set up triggers and actions that respond to customer behavior, ensuring timely and relevant communication.
Utilize the ActiveCampaign Dashboard Template to optimize your CRM strategies and drive business growth through targeted email marketing and automation.


