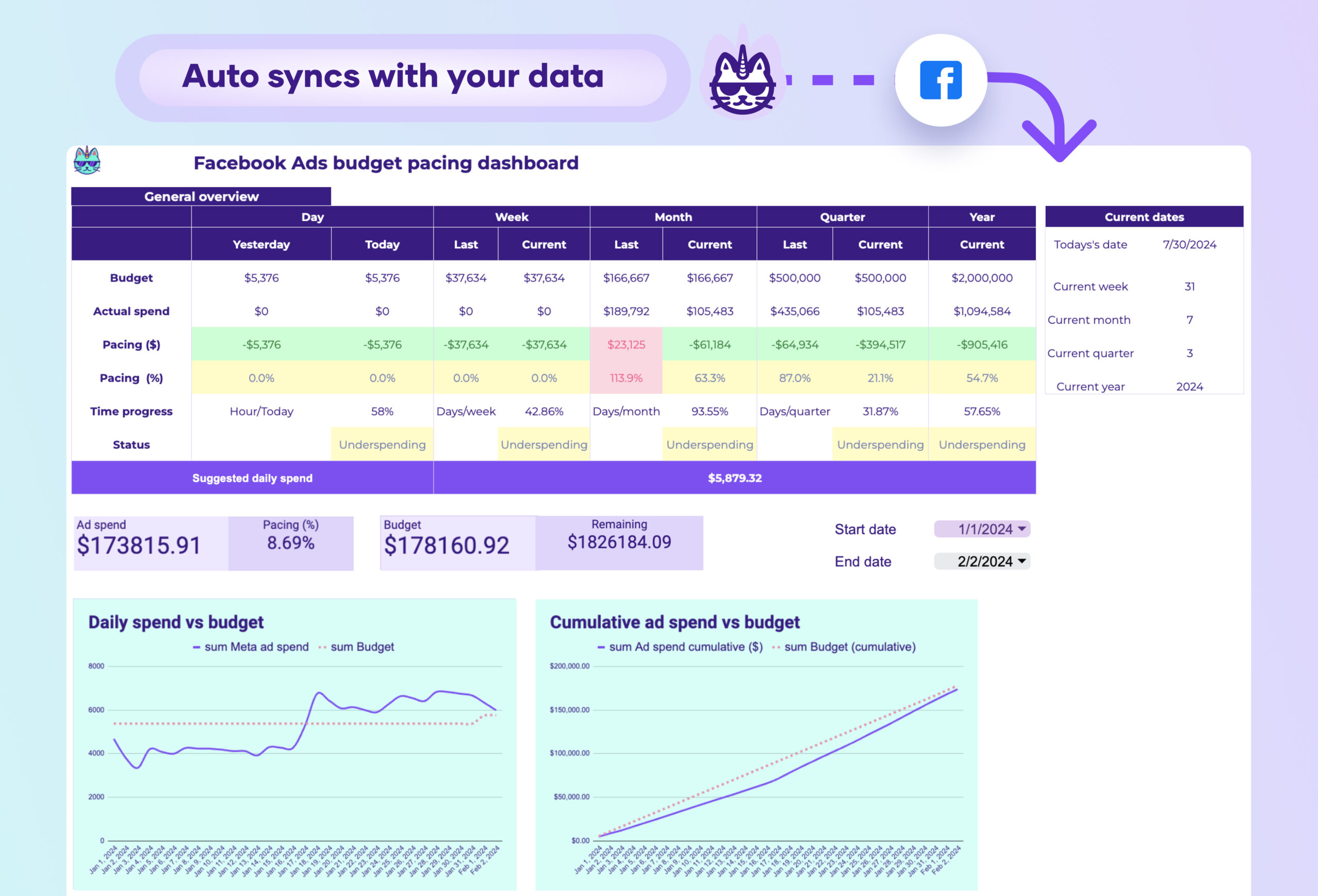
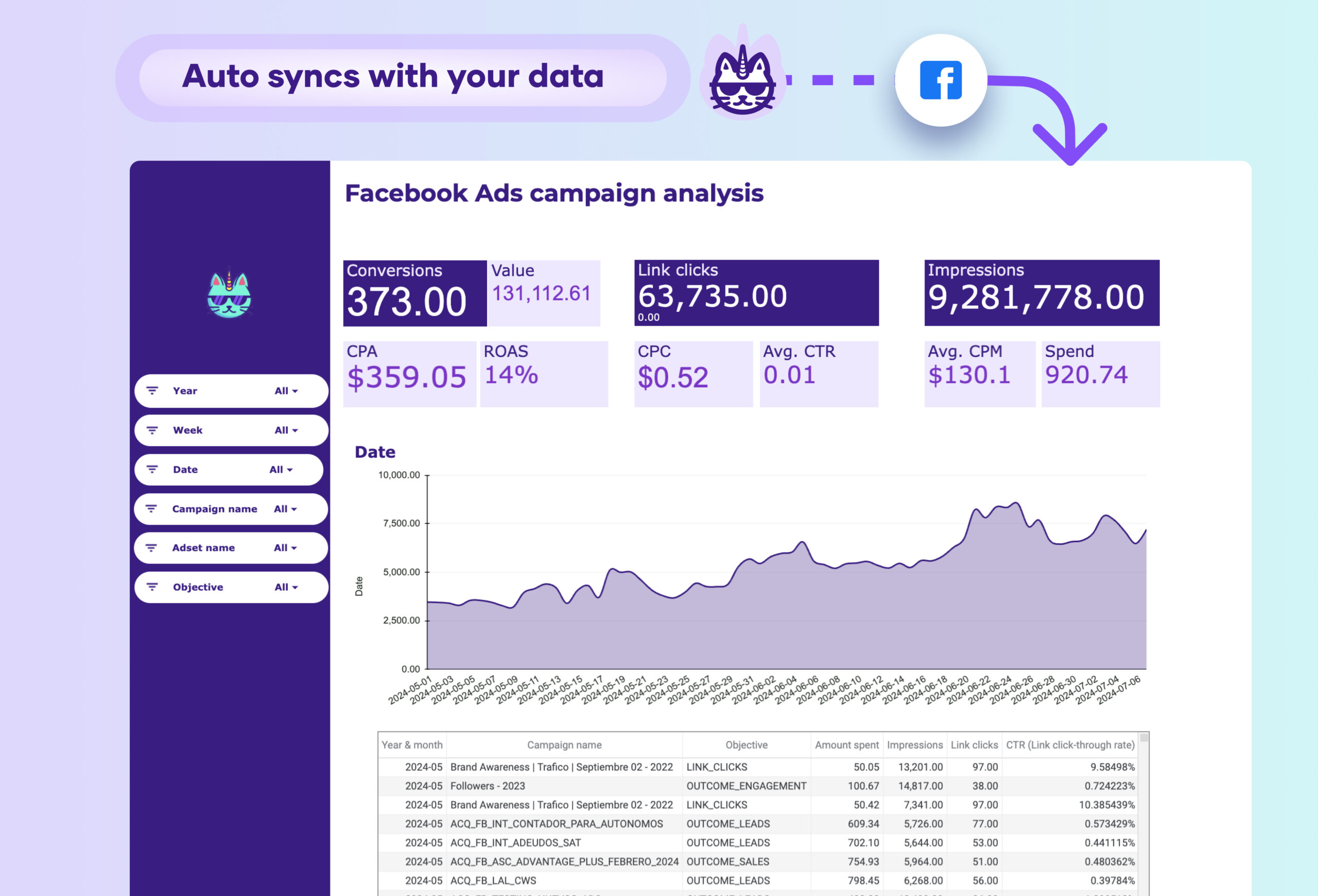
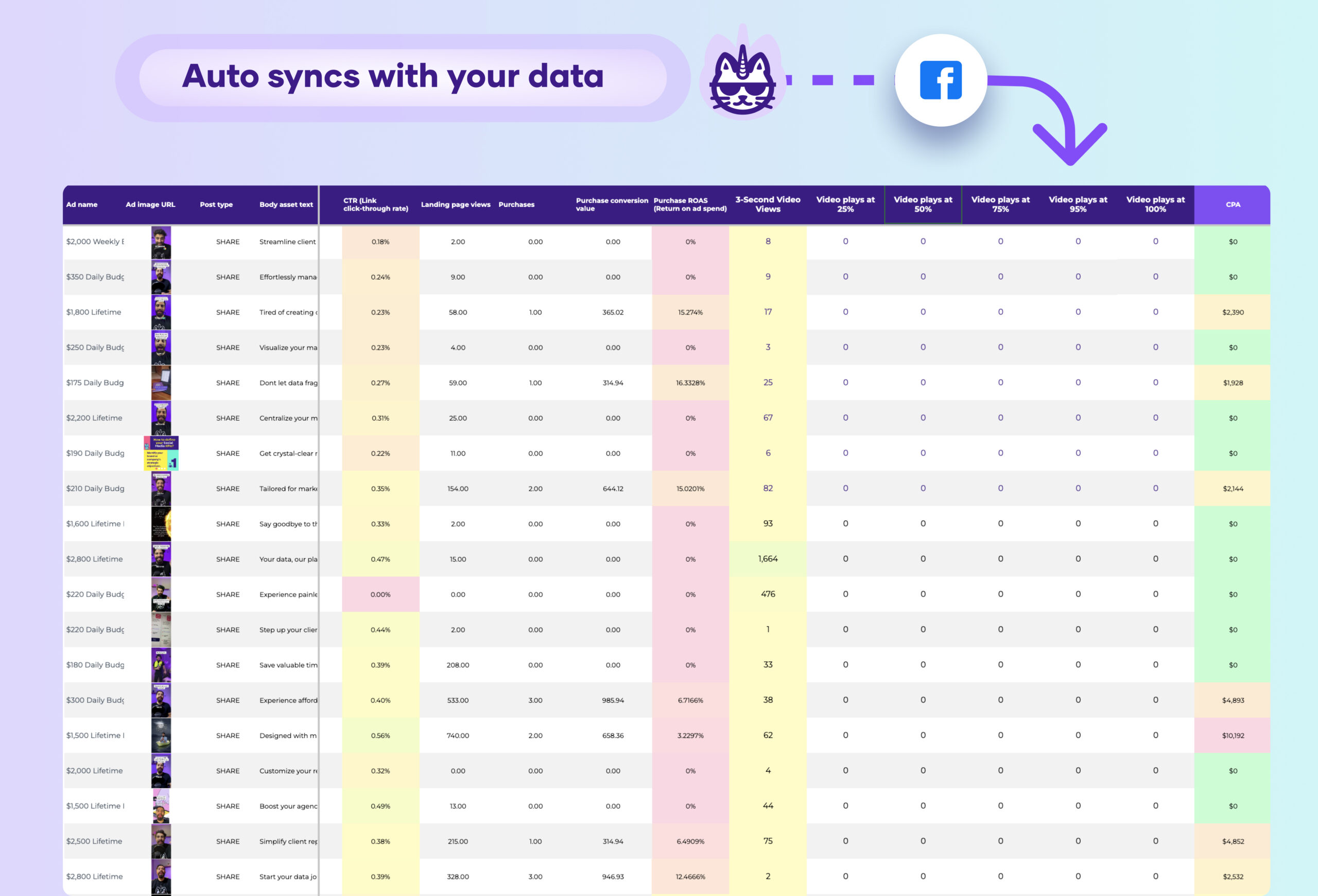
What is a budget tracking and pacing dashboard?
A budget tracking and pacing dashboard is an interface tool that consolidates data from multiple sources (e.g., accounting software, financial databases, spreadsheets) to track and display key performance indicators (KPIs) (e.g., budget utilization, variance, forecast accuracy), enabling teams and organizations to monitor financial performance and create presentations for stakeholders and executives.
Budget tracking dashboards are typically built using flexible tools like Google Looker Studio, Power BI, Google Sheets, or platform-specific solutions to enable high customization and integration of multiple data sources.
What to include in a budget tracking and pacing dashboard?
An actionable budget tracking dashboard balances context and specificity based on the audience (executives, managers, and analysts) and their use cases.
Executive budget dashboards
Executive dashboards for CFOs, CEOs, and stakeholders show the financial impact. Reviewed weekly, monthly, or quarterly, they include:
- Budget variance analysis: by department or project, using variance analysis for large budgets.
- Financial health metrics: cash flow, net income, and profitability ratios
- Forecast accuracy: comparison of actual vs. forecasted financials
- Add text for additional context to translate metrics for non-technical audiences. Present in slide decks and simplified Looker Studio reports.
Manager budget dashboards
Manager dashboards have cross-department views with drill-downs to see performance by project, team, region, and time period. They help align teams, define strategies, and include:
- Cross-department reporting: overall financial performance by department or project
- Goal tracking: compare current financial performance vs objectives
- Audits for prioritization and spotting issues
- Benchmarking for financial performance comparison
- Expense and revenue analysis
Operational Budget Dashboards
Operational dashboards for analysts and financial managers have granular, customizable KPIs to solve technical issues. Monitored hourly, daily, or weekly, they cover:
- Expense tracking: budget pacing, cost centers, expense categories
- Revenue tracking: income streams, sales performance
- Cash flow: inflows, outflows, liquidity metrics
- Forecasting: predictive analytics, trend analysis
Operational budget dashboards are highly customized, built in flexible tools like Google Sheets or Looker Studio to enable data cleaning, blending, annotations, and integrating multiple sources.
How to build a budget tracking and pacing dashboard?
To build a budget tracking dashboard, connect your data sources, choose a template on Looker Studio or Sheets, build your queries by selecting metrics and dimensions, choose charts to visualize your data, customize the dashboard, design and share via link, PDF or email.
Here’s the breakdown:
Connect data sources
Define and connect the data sources to bring to your dashboard. Common sources are accounting software, financial databases, CRM for sales data, and spreadsheets for manual entries.
To connect your data sources, go to portermetrics.com, choose the data sources to bring to your dashboard.
You can follow these tutorials on connecting your data:
Choose a template
Choose from dozens of budget tracking dashboard templates in Google Sheets or Looker Studio, designed for use cases like budget monitoring, financial forecasting, and expense management.
Learn to copy Looker Studio templates.
While templates are the starting point. Make them specific for your business or organization. Map your specific metrics, especially custom financial metrics, CRM sales data, and all the fields and metrics that you define as "expenses" and "revenue".
Depending on your reporting tool—Google Sheets or Google Looker Studio, pick any of the dozens of templates created by our team and customers to solve your financial reporting use cases, such as budget monitoring, financial forecasting, and expense management.
Select metrics, dimensions, and charts
Once your dashboard template is downloaded, you may 1)modify it or 2) create a blank page to build it from scratch. Whatever the case, setting up a query always follows these steps:
- Select the data source and the account connected to it
- Choose metrics (e.g. Expenses, Revenue, Cash Flow, etc.).
- Choose breakdowns to segment your data (e.g. by date, department, project, etc.)
You can follow these tutorials on adding data to your dashboards
Design
To make your budget tracking dashboards truly white-label you can add logos, colors, fonts, and styling to mirror your brand.
Follow these tutorials to design your budget tracking dashboards:
Share
Share your budget tracking dashboards via links, PDF, schedule emails, and control permissions.
KPIs to include in a budget tracking and pacing dashboard?
Budget tracking dashboards should include a mix of financial performance, efficiency, effectiveness, revenue, and cost metrics and KPIs to fully understand the financial health and performance towards business goals. They include:
Financial performance KPIs measure the financial process, regardless of the department:
- Budget metrics: budget utilization, variance, forecast accuracy
- Expense metrics: operating expenses, cost of goods sold, overhead costs
- Revenue metrics: sales revenue, recurring revenue, key income streams
Efficiency KPIs compare your financial outputs to the cost, including:
- Expense: cost per unit, cost per project
- Revenue: revenue per unit, revenue per project
- Profitability: gross margin, net margin
Effectiveness KPIs compare the input with the output from one financial stage to another
- Expense: cost control, budget adherence
- Revenue: revenue growth rate, sales efficiency
- Profitability: return on investment, return on assets
Financial and cost KPIs show the bottom-line impact of your financial performance:
- Financial: net income, EBITDA
- Cost: total expenses, capital expenditures
- Efficiency: ROI, cost efficiency
- Effectiveness: profit margin, asset turnover
To analyze these financial KPIs, segment them by:
- Department: finance, operations, sales
- Time: Hourly, daily, weekly, monthly
- Project: phase, objective
- Business: branch, region, division
- Category: expense type, revenue stream
- Source: internal, external, funding